Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure performed to rebuild a woman’s breast(s) after a mastectomy or, in some cases, a lumpectomy. These surgeries aim to restore the breast’s shape, size, and symmetry. Breast reconstruction can be an essential part of the recovery process for women who have undergone breast cancer treatment. Here are key aspects of this procedure:
Types of Breast Reconstruction:
- Autologous Tissue Reconstruction (Flap Procedures):
TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Muscle): Uses muscle, fat, and skin from the abdomen.
DIEP Flap (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator): Similar to TRAM but spares the abdominal muscle.
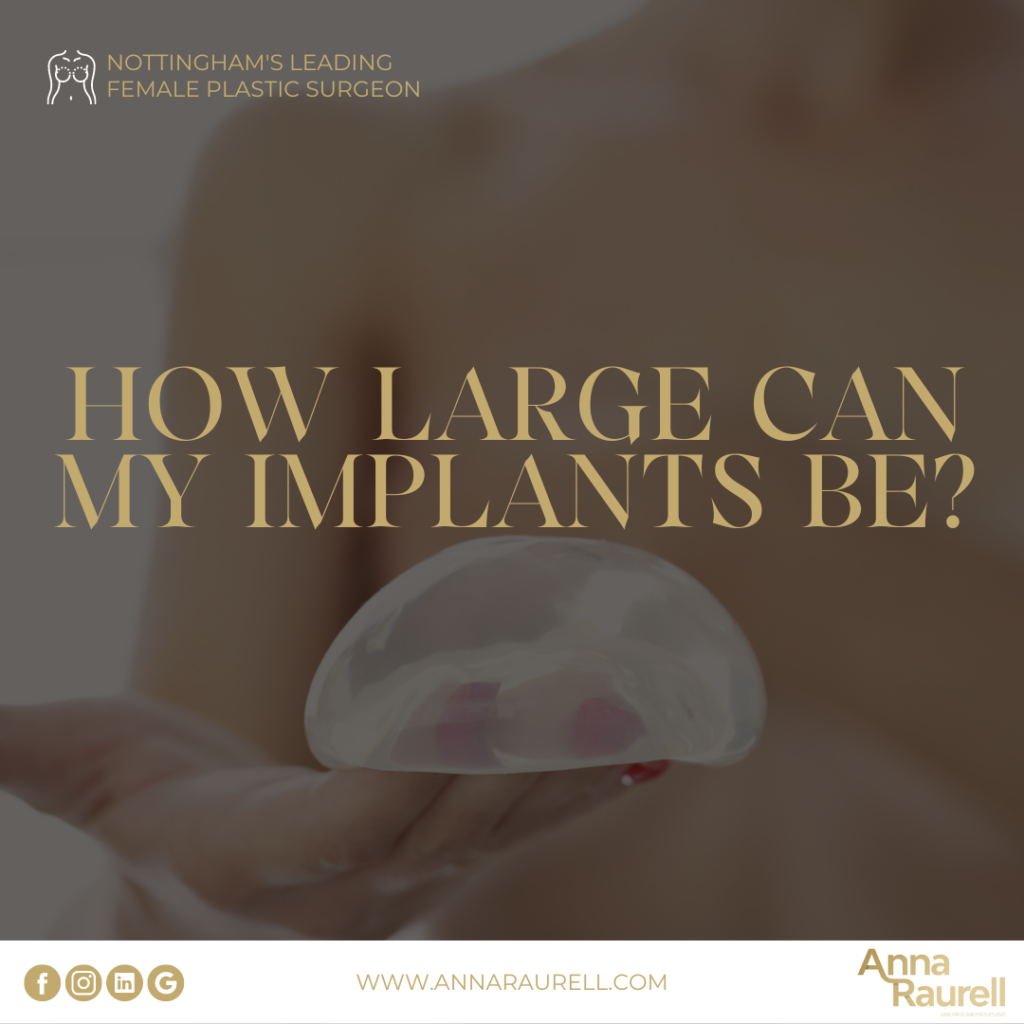
- Implant-Based Reconstruction:
Uses breast implants to reconstruct the breast shape. It may involve a tissue expander to stretch the skin gradually.
- Combination Reconstruction:
Combines autologous tissue and implants for a more customised approach.
Timing of the procedure:
- Immediate Reconstruction:
Performed at the same time as the mastectomy.
- Delayed Reconstruction:
Conducted weeks, months, or even years after mastectomy or lumpectomy.
Considerations:
- Patient’s Health Status:
The patient’s overall health, cancer treatment plan, and personal preferences influence the timing and type of reconstruction.
- Cancer Treatment Considerations:
The need for radiation therapy may affect the type and timing of reconstruction.
- Personal Preferences:
Patient preferences, lifestyle, and individual goals play a significant role in the decision-making process.
Additional Procedures:
- Nipple and Areola Reconstruction:
Often performed as a separate procedure to recreate a natural-looking nipple and areola.
- Symmetry Procedures:
Adjustments to the opposite breast for better symmetry, which may include reduction, lift, or augmentation.
Emotional and Psychological Considerations:
- Support:
Emotional support, counseling, and involvement of support groups can be beneficial.
- Realistic Expectations:
Patients should have realistic expectations regarding the outcomes of breast reconstruction.
Reconstruction After Lumpectomy:
- Oncoplastic Surgery:
Combining tumor removal with plastic surgery techniques to preserve the breast’s appearance.
- Partial Breast Reconstruction:
Filling in the defect left after lumpectomy using various techniques.
Breast reconstruction is a personal decision, and the choice depends on individual circumstances, medical considerations, and personal preferences. It’s crucial for individuals to consult with a plastic surgeon experienced in breast reconstruction to explore options, understand potential outcomes, and make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and goals.
To book in for your consultation with Anna Raurell please contact us here.